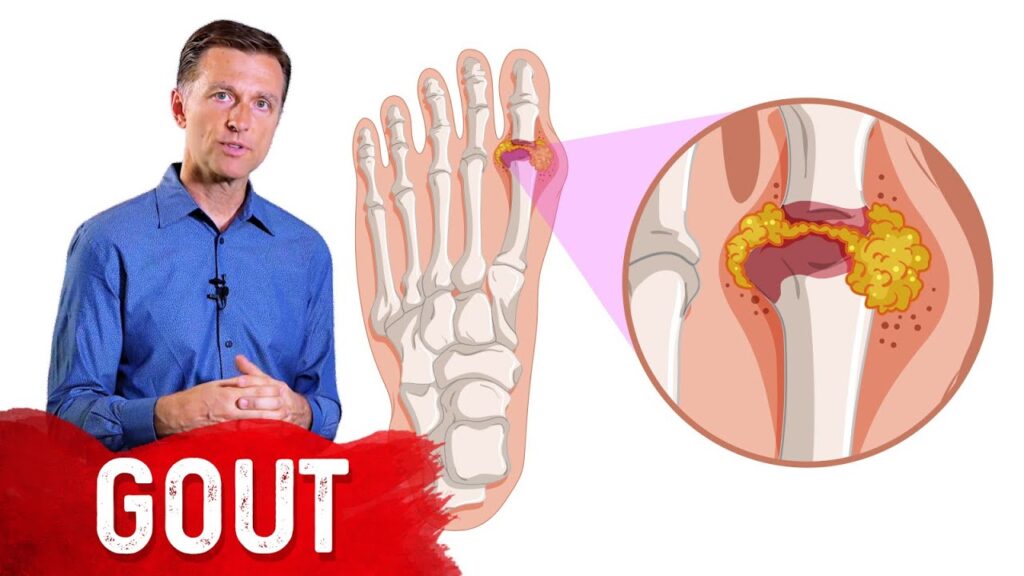
Gout is a painful form of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. A gout attack can occur suddenly, often at night, and may lead to intense pain, swelling, redness, and stiffness in the affected joint. If you are experiencing a gout attack, there are steps you can take to alleviate the pain and reduce the duration of the flare-up. Here’s a comprehensive guide to stopping a gout attack and preventing future episodes.
Immediate Steps During a Gout Attack
- Rest the Affected Joint:
- Avoid putting pressure on the affected joint.
- Keep the joint elevated to reduce swelling and inflammation.
- Apply Ice Packs:
- Place an ice pack or a cold compress on the affected joint for 15-20 minutes every hour.
- Wrap the ice pack in a towel to avoid direct contact with the skin.
- Stay Hydrated:
- Drink plenty of water to help flush excess uric acid from your body.
- Avoid sugary drinks and alcohol, as they can exacerbate gout symptoms.
- Take Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Avoid aspirin, as it may worsen gout by increasing uric acid levels.
- Use Prescription Medications (if available):
- Colchicine: Helps reduce pain and inflammation during a gout attack.
- Corticosteroids: Prednisone or other corticosteroids may be prescribed to quickly reduce inflammation if NSAIDs are not effective.
Dietary Adjustments During a Gout Attack
- Avoid High-Purine Foods:
- Purines are substances that break down into uric acid. Avoid foods high in purines, such as:
- Red meat (beef, lamb, pork).
- Organ meats (liver, kidneys, brain).
- Shellfish (shrimp, lobster, mussels).
- Certain fish (sardines, anchovies, mackerel).
- Purines are substances that break down into uric acid. Avoid foods high in purines, such as:
- Consume Low-Purine Foods:
- Focus on foods that are less likely to increase uric acid levels, such as:
- Low-fat dairy products.
- Whole grains.
- Vegetables (except those high in purines like spinach and asparagus, though their effect is less significant).
- Focus on foods that are less likely to increase uric acid levels, such as:
- Incorporate Cherries and Cherry Juice:
- Cherries contain compounds that may help reduce uric acid levels and inflammation.
- Drink unsweetened cherry juice or eat fresh cherries during a gout attack.
- Limit Alcohol and Sugary Beverages:
- Beer, wine, and sugary sodas can increase uric acid levels and worsen gout symptoms.
Preventing Future Gout Attacks
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Excess weight increases the risk of gout. Losing weight gradually can help lower uric acid levels.
- Stay Active:
- Regular exercise can improve joint health and overall well-being.
- Avoid strenuous activities during a gout attack to prevent further irritation.
- Follow a Gout-Friendly Diet:
- Stick to a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Avoid high-purine and processed foods.
- Stay Hydrated:
- Drink at least 8-10 glasses of water daily to help flush out uric acid.
- Monitor Uric Acid Levels:
- Work with your healthcare provider to track your uric acid levels and keep them within the normal range (below 6 mg/dL for most people).
- Take Preventive Medications (if prescribed):
- Allopurinol: Reduces the production of uric acid.
- Febuxostat: Another medication that lowers uric acid levels.
- Probenecid: Helps the kidneys excrete uric acid more effectively.
When to See a Doctor
- If this is your first gout attack.
- If symptoms do not improve within a few days despite treatment.
- If the pain becomes unbearable or you develop a fever, which could indicate an infection.
- If you experience frequent gout attacks, as this may require long-term management.
Conclusion
A gout attack can be debilitating, but taking immediate action can help reduce pain and inflammation. By resting the affected joint, staying hydrated, and using medications or home remedies, you can alleviate symptoms more quickly. To prevent future attacks, focus on lifestyle changes, a gout-friendly diet, and maintaining healthy uric acid levels. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized treatment and guidance.