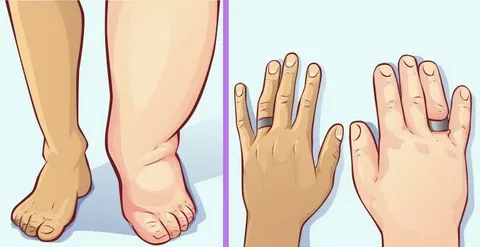
Water retention, also known as fluid retention or edema, occurs when excess fluid builds up in the body’s tissues. It can cause swelling in various parts of the body, such as the hands, feet, legs, and abdomen. While it’s often temporary and harmless, chronic water retention could be a sign of an underlying health issue. Understanding the causes can help you manage and reverse it effectively. Here are six common causes and tips for addressing them.
1. High Sodium Intake
Sodium is an essential mineral that helps balance fluids in your body. However, consuming too much salt can cause your body to retain water to balance sodium levels.
How to Reverse It:
- Reduce your intake of processed and packaged foods, which are often high in salt.
- Cook with herbs and spices instead of salt for flavor.
- Drink plenty of water to help flush out excess sodium.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during the menstrual cycle or pregnancy, can lead to water retention. This is due to changes in progesterone and estrogen levels, which affect the body’s fluid balance.
How to Reverse It:
- Engage in regular exercise to promote circulation.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in potassium and magnesium to regulate hormone levels.
- Consider speaking to a healthcare professional if hormonal water retention is severe.
3. Physical Inactivity
Sitting or standing for long periods can cause blood flow to slow, leading to water retention, especially in the lower extremities.
How to Reverse It:
- Take breaks to move around and stretch every hour.
- Elevate your legs periodically to encourage fluid drainage.
- Wear compression stockings if you experience persistent swelling in your legs.
4. Dehydration
When your body is dehydrated, it may retain water as a protective mechanism. Ironically, not drinking enough water can make water retention worse.
How to Reverse It:
- Drink 8-10 glasses of water daily, or more if you’re active or in a hot climate.
- Avoid excessive caffeine and alcohol, which can dehydrate you.
- Include hydrating foods like cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges in your diet.
5. Medications
Certain medications, such as corticosteroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and blood pressure medications, can cause water retention as a side effect.
How to Reverse It:
- Speak to your doctor about adjusting your medication or exploring alternatives.
- Stay hydrated and maintain an active lifestyle to minimize side effects.
- Monitor your symptoms and report any significant changes to your healthcare provider.
6. Underlying Health Conditions
Chronic water retention can sometimes be linked to medical conditions such as kidney disease, heart failure, or liver issues. These conditions affect the body’s ability to manage fluids effectively.
How to Reverse It:
- Consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation if you suspect a medical condition.
- Follow your doctor’s treatment plan and dietary recommendations.
- Monitor your symptoms closely and seek immediate medical attention if swelling worsens or is accompanied by other symptoms like shortness of breath.
General Tips to Prevent and Manage Water Retention
- Increase Potassium Intake: Foods like bananas, avocados, and sweet potatoes can help balance sodium levels.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity improves circulation and reduces fluid buildup.
- Limit Carbohydrate Intake: High-carb diets can cause water retention because carbs are stored with water in the body.
- Use Natural Diuretics: Foods like parsley, dandelion, and green tea can help reduce fluid retention naturally.
Water retention can be an uncomfortable experience, but with lifestyle changes and a better understanding of its causes, it’s often manageable. If your symptoms persist or worsen, always consult a healthcare professional for guidance.