Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of your nerves, blood cells, and DNA synthesis. Despite its importance, vitamin B12 deficiency is surprisingly common, especially among older adults, vegans, and individuals with certain medical conditions. Alarmingly, many people remain unaware of their deficiency because the symptoms can be subtle and often mistaken for other conditions. Recognizing these signs is the first step toward addressing the issue.
Fatigue and Weakness
One of the earliest and most common symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency is fatigue. Without enough B12, your body struggles to produce sufficient red blood cells, which are necessary for transporting oxygen throughout the body. This can lead to persistent tiredness, even after adequate sleep, and a general sense of weakness. If you find yourself constantly exhausted without a clear reason, it might be worth checking your B12 levels.
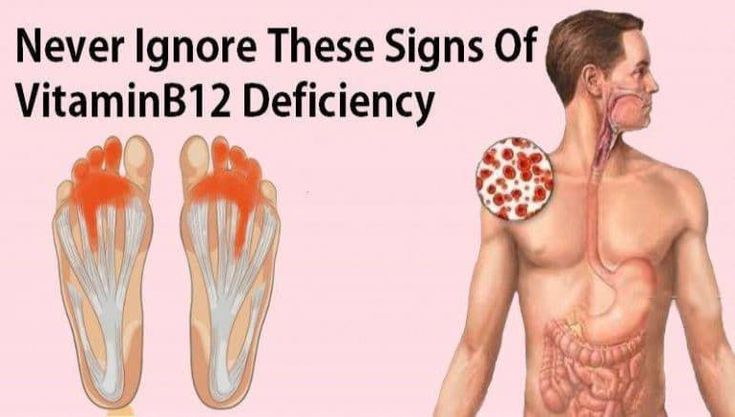
Numbness and Tingling
Vitamin B12 is vital for the health of your nervous system. A deficiency can cause nerve damage, leading to sensations of numbness, tingling, or pins-and-needles, particularly in the hands and feet. Over time, untreated B12 deficiency can result in more severe nerve-related symptoms, such as difficulty walking or maintaining balance.
Cognitive Impairments
Brain fog, memory problems, and difficulty concentrating are also common symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency. These cognitive issues are often overlooked or attributed to aging, stress, or other factors. However, they may signal a deficiency that, if addressed early, can prevent further neurological damage.
Pale or Jaundiced Skin
Individuals with B12 deficiency may develop pale or yellow-tinged skin, a condition known as jaundice. This occurs because a lack of B12 affects red blood cell production, leading to their premature breakdown and the release of bilirubin, a substance that gives skin a yellowish hue.
Glossitis and Mouth Ulcers
Glossitis, or an inflamed tongue, can be a telling sign of B12 deficiency. The tongue may appear red, swollen, and smooth, often accompanied by pain and difficulty speaking or eating. Some people may also develop mouth ulcers or a burning sensation in the mouth.
Mood Changes and Depression
Vitamin B12 deficiency has been linked to mood disturbances, including irritability, anxiety, and depression. This is because B12 plays a role in synthesizing neurotransmitters like serotonin, which regulate mood. Addressing the deficiency can often lead to significant improvements in mental health.
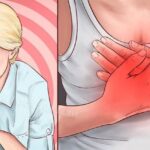
Heart Palpitations and Shortness of Breath
Low levels of B12 can affect your cardiovascular system, causing symptoms like heart palpitations and shortness of breath. These symptoms are often linked to anemia, which reduces the oxygen supply to your tissues.
Risk Factors for Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Certain groups of people are more at risk of developing vitamin B12 deficiency. These include:
- Vegans and Vegetarians: Since B12 is primarily found in animal-based foods, individuals following plant-based diets may not get enough of this nutrient.
- Older Adults: Aging can reduce the body’s ability to absorb B12 due to decreased stomach acid production.
- Individuals with Digestive Disorders: Conditions like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, or gastritis can interfere with B12 absorption.
- People Taking Certain Medications: Long-term use of antacids or metformin can impair B12 absorption.
Diagnosing and Treating Vitamin B12 Deficiency
If you suspect a vitamin B12 deficiency, consult a healthcare provider. Diagnosis typically involves a blood test to measure B12 levels. Treatment depends on the severity of the deficiency and may include dietary changes, oral supplements, or B12 injections. Common food sources of vitamin B12 include meat, fish, eggs, dairy products, and fortified cereals.
Conclusion
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a hidden health concern that can lead to a wide range of symptoms, from fatigue and numbness to cognitive decline and mood disorders. Early recognition and treatment are key to preventing long-term complications. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above or belong to a high-risk group, consider discussing your B12 levels with a healthcare provider. Taking proactive steps can help ensure you maintain optimal health and well-being.