Sleep is an essential part of life, contributing to physical, mental, and emotional well-being. While much attention is given to the quality and duration of sleep, the position you sleep in can also play a significant role in your overall health. Different sleeping positions can impact everything from your posture to your digestion, and even your risk of developing certain medical conditions. Here, we explore how your sleeping position can affect your health and what you can do to optimize it.
The Most Common Sleeping Positions
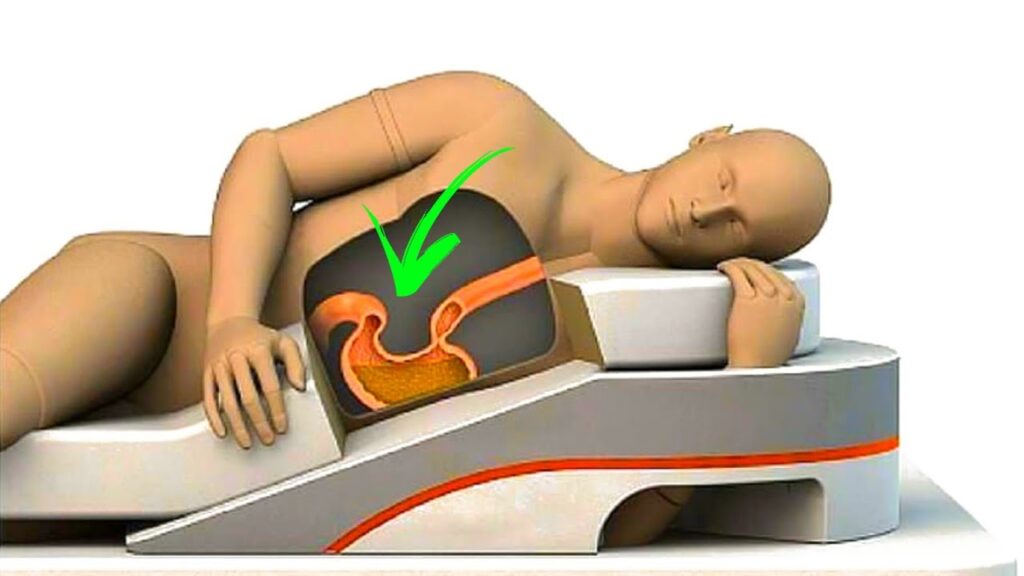
- Back Sleeping (Supine Position): Sleeping on your back with your head and neck aligned is often recommended by health professionals. This position helps maintain the natural curve of the spine, reducing the risk of back and neck pain. It also minimizes pressure on joints, making it ideal for people with arthritis. However, back sleeping can exacerbate snoring and sleep apnea because gravity causes the tongue to fall backward, partially obstructing the airway.
- Side Sleeping: Side sleeping is the most common position and is often praised for its health benefits. It can reduce snoring, alleviate acid reflux, and improve digestion. Side sleeping on the left side, in particular, is thought to benefit heart health by reducing pressure on the heart and improving circulation. However, it can sometimes cause shoulder stiffness or exacerbate wrinkles due to facial compression against the pillow.
- Fetal Position: This variation of side sleeping, where the body is curled up like a fetus, can provide comfort and reduce snoring. However, curling up too tightly may restrict diaphragmatic breathing and strain the neck and back. Ensuring a slightly looser fetal position can help mitigate these issues.
- Stomach Sleeping (Prone Position): Sleeping on your stomach is generally considered the least healthy position. It can strain the neck and spine, leading to discomfort and pain. Additionally, stomach sleeping can compress the lungs and restrict breathing. However, it might reduce snoring for some individuals by keeping the airway open.
Health Impacts of Sleeping Positions
- Spinal Alignment: Proper spinal alignment during sleep is crucial to preventing chronic back and neck pain. Back sleeping is often the best for maintaining alignment, provided you use a supportive mattress and pillow. Side sleeping can also support alignment if the knees are bent slightly and a pillow is placed between them.
- Breathing and Snoring: Your sleeping position can significantly impact your breathing. Back sleeping tends to worsen snoring and obstructive sleep apnea, while side sleeping can alleviate these conditions by keeping the airway open. If you struggle with sleep apnea, side sleeping or using an elevated pillow may help.
- Digestive Health: Side sleeping, particularly on the left side, has been shown to improve digestion and reduce acid reflux. This is because the position allows gravity to aid the movement of food through the digestive tract and prevents stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus.
- Circulation: Sleeping on your left side can improve circulation by reducing pressure on the vena cava, a large vein that carries blood back to the heart. Pregnant women are often advised to sleep on their left side to enhance blood flow to the fetus.
- Wrinkles and Skin Health: Stomach and side sleeping can cause facial compression, which may lead to wrinkles over time. If you’re concerned about skin health, consider using a silk pillowcase or sleeping on your back.
Tips for Optimizing Your Sleeping Position
- Invest in the Right Pillow: A supportive pillow can help maintain proper alignment of the neck and spine. Side sleepers may benefit from a firmer pillow, while back sleepers often prefer medium support.
- Use a Body Pillow: For side sleepers, a body pillow can help align the spine and reduce pressure on the hips and shoulders.
- Elevate Your Head: If you’re a back sleeper prone to snoring, using an adjustable bed or an elevated pillow can help keep your airway open.
- Train Yourself to Sleep in a Healthier Position: If your preferred position causes discomfort or health issues, try gradually training yourself to sleep in a different position using pillows for support.
- Choose the Right Mattress: A mattress that supports your natural curves is crucial for all sleeping positions. Side sleepers may need a softer mattress to cushion their shoulders and hips, while back sleepers often benefit from medium-firm options.
Final Thoughts
Your sleeping position is more than just a matter of comfort—it’s an integral part of your overall health. While no single position is perfect for everyone, understanding how different positions affect your body can help you make informed decisions about your sleep habits. By optimizing your sleeping position and investing in the right sleep accessories, you can improve not only your sleep quality but also your long-term health and well-being.